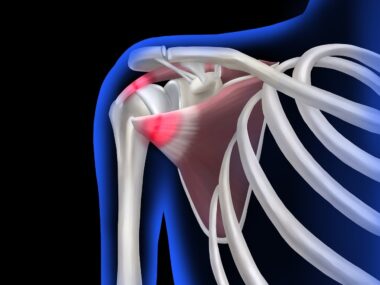
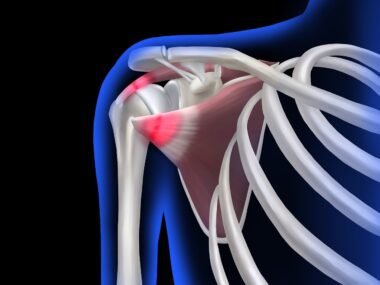
Pediatric Shoulder Injuries in Sports: Diagnosis and Management
Pediatric athletes frequently experience shoulder injuries, which can have serious implications for their development and participation in sports. Common injuries include rotator cuff tears, shoulder dislocations, and overuse injuries. These problems typically arise during activities that involve repetitive overhead motions, such as swimming and throwing sports. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent long-term consequences affecting athletic performance and growth. Parents and coaches should understand the signs of shoulder injuries, including pain, swelling, and limited range of motion. If any of these symptoms occur, it is essential to promptly consult a medical professional. In many cases, conservative treatments like physical therapy and rest can effectively alleviate symptoms. Understanding the importance of seeking medical advice is crucial for young athletes wishing to return to their sports safely. This article explores the diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies for pediatric shoulder injuries. By enhancing awareness among families and coaches, we can ensure that young athletes receive appropriate care and can maximize their performance while minimizing the risk of serious injuries.
Diagnosis of shoulder injuries in young athletes often involves a thorough examination and imaging tests. Physicians usually begin with a detailed patient history, reviewing the athlete’s symptoms and the mechanism of injury. Following this, a physical examination assesses the shoulder’s range of motion and strength. Radiographic evaluations, including X-rays or MRIs, may be required to confirm the diagnosis. These imaging techniques help visualize the anatomical structures of the shoulder, revealing fractures, soft tissue injuries, or degenerative changes. Identifying the exact nature of the injury is critical as it directly influences treatment options. A comprehensive diagnostic approach aids healthcare providers in creating tailored management plans for each athlete. Sports medicine specialists must understand the nuances of pediatric shoulder injuries due to growth factors and the active lifestyle of children. Treatment protocols often include a combination of medication, therapeutic exercises, and potentially, surgical interventions for more severe cases. By prioritizing accurate diagnoses, healthcare professionals can better address the unique needs of young athletes seeking to recover quickly and return to their favorite sports activities.
Typical Shoulder Injuries in Pediatrics
Among pediatric athletes, specific shoulder injuries are more prevalent and warrant focused attention. Rotator cuff tears are a common concern and typically result from repetitive overhead activity, leading to wear and tear of the shoulder’s fibers. A labral tear is another injury that often occurs in throwing athletes due to the high stress placed on the shoulder during their motions. Impingement syndrome can also develop in young athletes, particularly in sports that involve arching or reaching. Moreover, shoulder dislocations are particularly alarming, as they often necessitate immediate medical attention and can lead to chronic instability. Overuse injuries in the shoulder are frequently observed as well, impacting young players through continual strain on developing tissues. Effective management of these injuries relies on prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment protocols tailored to young athletes’ needs. Each injury requires a distinct approach that encompasses education on prevention and rehabilitation, fostering resilience in their sports journey. Youth athletes can benefit significantly from knowledge and resources regarding shoulder health through innovative training practices and enhanced awareness of injury signs and symptoms.
Management of shoulder injuries in pediatric athletes typically includes various treatment modalities, ranging from conservative measures to surgical interventions. Traditional methods often consist of rest, ice application, and anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate pain and swelling. Physical therapy plays a fundamental role, focusing on restoring strength and flexibility, which are critical for recovery. In severe cases, surgical procedures may be required to repair injuries like labral tears or rotator cuff damage. Following any surgical intervention, a rigorous rehabilitation program is essential for optimal recovery. This program could involve gradual strength training and gradual return to sports activities based on individual progress. The objective is to make a safe and effective transition back to play, reducing the risk of re-injury. Furthermore, it is crucial to implement strategies to prevent future injuries. Educating young athletes and their coaches on proper technique, body mechanics, and strength conditioning helps promote shoulder safety. Regular screening for flexibility and strength can identify at-risk individuals before they sustain injuries. By integrating comprehensive management strategies, we can significantly enhance the well-being of pediatric athletes throughout their sporting journey.
Rehabilitation Strategies for Pediatric Athletes
Rehabilitation strategies for pediatric shoulder injuries are crucial in helping young athletes regain full function while ensuring long-term shoulder health. The initial phase of rehabilitation typically focuses on reducing pain and inflammation through rest, ice, and gentle mobility exercises. As healing progresses, the rehabilitation program should transition toward strengthening the shoulder muscles that support stability. This may involve targeted resistance training, focusing on rotator cuff strength, scapular control, and shoulder range of motion exercises. Incorporating sport-specific drills towards the later stages of rehabilitation ensures that athletes can safely prepare for a return to their sporting activities with minimal risk. Additionally, integrating proprioceptive and balance exercises can enhance body awareness, further reducing the risk of re-injury during play. Regular follow-ups with a sports medicine specialist or physical therapist can help track progress, adjust rehabilitation protocols, and address any arising concerns. Moreover, educating young athletes on self-monitoring practices can empower them to recognize symptoms early, facilitating timely intervention. By prioritizing comprehensive rehabilitation approaches, healthcare providers can significantly improve pediatric athletes’ outcomes, enhancing both their performance and confidence.
Prevention of shoulder injuries in pediatric athletes requires a multifaceted approach involving athletes, coaches, and parents. Educating young athletes about proper techniques and mechanics is critical to reducing injury risks during training and competition. Utilizing warm-up routines can help prepare the shoulder joint for the demands of overhead activities. Strengthening the core and shoulder muscles through integrated training programs can enhance stability and resilience, further mitigating chances of injury. Coaches should emphasize the importance of listening to athletes about pain or discomfort, encouraging open communication about their physical condition. Moreover, adhering to sports-specific regulations regarding pitch counts or play frequency can help minimize overuse injuries. Regular screenings for flexibility and strength are also recommended to identify athletes who may be at higher risk for shoulder injuries. Ultimately, fostering a safety-first culture among young athletes can contribute significantly to injury prevention. By promoting awareness and proactive measures, stakeholders can create an environment that supports both physical well-being and athletic development. Collectively, these preventive strategies can lay the foundation for a healthier sporting experience for all young athletes.
Conclusion
Pediatric shoulder injuries pose challenging dilemmas for young athletes and their support systems. Understanding the diagnosis, management, and prevention of these injuries can foster a healthier environment for sports participation. Early intervention is vital for minimizing long-term effects, while tailored treatment plans ensure athletes regain their pre-injury capabilities. Families must educate themselves about injury signs and promote open communication between young athletes and their coaches. By implementing robust rehabilitation strategies, healthcare providers can facilitate a safe return to play, while preventive measures will support a generation of strong and resilient young athletes. Overall, the role of physical education and sports medicine professionals is invaluable in nurturing a culture of safety and performance excellence. Young athletes deserve comprehensive care that prioritizes their health and personal development in sports. The collaborative effort among families, coaches, and healthcare specialists can make significant strides in safeguarding youth athletes against shoulder injuries. As we continue to learn more about sports medicine, it is essential to remain committed to improving understanding and implementation of effective strategies in managing and preventing pediatric shoulder injuries.
For additional resources and information on pediatric sports medicine, athletes and their families are encouraged to explore reputable websites and literature. Resources such as AAOS (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons) offer guidance on injury prevention and management. Young athletes should also be aware of organizations that focus specifically on their needs, helping ensure they receive appropriate training and care. As community awareness increases, opportunities for engagement with health and sports professionals can enhance educational resources. From workshops to fitness programs, families can partake in initiatives that promote shoulder health and overall athletic performance. Lastly, maintaining a proactive dialogue with healthcare providers can aid in tracking developments in injury management practices. Incorporating regular wellness checks can lead to early diagnosis and better outcomes for young athletes. By empowering families with knowledge and accessible information, we can cultivate a robust network that supports the health and well-being of children involved in sports. Together, we can inspire a safer and more enjoyable sporting experience for the next generation of athletes.