Core Stabilization Techniques for Gymnasts
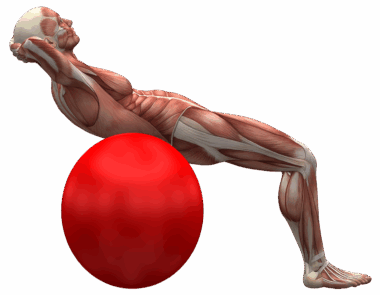
Core stabilization is crucial in gymnastics, as it enhances performance and reduces injury risk. Gymnasts rely on their core muscles to maintain balance during routines. These muscles stabilize the spine and pelvis, ensuring efficient movement. One effective technique for core stabilization is focused breathing. This method involves inhaling deeply, engaging the diaphragm, and holding the core tight while exhaling. Additionally, exercises like planks and bridges help strengthen the core. Planks engage multiple core muscles, while bridges emphasize the glutes and lower back. Incorporating these exercises into a training regimen can lead to significant strength improvements. Furthermore, rotational movements, such as medicine ball twists, enhance the obliques and improve trunk rotation, essential for gymnastics. In order to optimize core training, gymnasts should also prioritize proper alignment. This means maintaining a neutral spine during exercises to prevent injury. Finally, incorporating balance tools like stability balls or Bosu balls can further challenge core stability. Therefore, understanding various techniques and exercises is key for gymnasts aiming to improve core stability and overall performance. Consistent training using these methods supports the development of a strong, functional core.
Balance and control are vital for gymnasts, as they execute complex movements. Enhancing core stability directly influences these abilities. One way to develop this is through proprioceptive training; this involves exercises that improve body awareness. For instance, using a balance beam can enhance stability while developing muscle coordination. Furthermore, integrating dynamic movements such as single-leg deadlifts helps strengthen the core while promoting balance. It’s essential to gradually increase the complexity of these exercises to provide a consistent challenge to the core system. Additionally, gymnasts should include stretching in their routines to maintain flexibility and range of motion. Techniques like Pilates and yoga focus on core strength while emphasizing alignment and flexibility, contributing to overall stability. Moreover, practicing gymnastic-specific movements can improve core stability. For instance, performing handspring drills strengthens the core while mimicking actual competition movements. Alongside this, gymnasts should track their progress, adjusting training based on individual needs and abilities. Lastly, combining strength training with functional movements ensures a comprehensive approach. Unless gymnasts actively work on core stabilization, their performance may be compromised. Therefore, these strategies are essential for developing a solid foundation in gymnastics.
Another integral aspect of core stabilization is understanding the role of different muscle groups. The core consists of more than just the abdominal muscles; it includes the muscles of the lower back, hips, and pelvic region. Strengthening this entire area supports the body’s overall stability during athletic performance. Exercises like bicycle crunches and Russian twists target these areas specifically. These movements not only build muscle strength but also improve coordination and reaction times, crucial for gymnastics. Additionally, gymnasts must pay attention to their nutrition to support muscle development. A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals supplies the nutrients needed for muscle recovery. Recovery is often overlooked yet vital for performance improvement. Incorporating active recovery days focusing on mobility and flexibility helps prevent overtraining and injuries. Furthermore, visualizing successful routines can also enhance performance, as mental preparation boosts confidence and focus. The mind-body connection plays a significant role in gymnastics; hence, techniques such as mindfulness and meditation can improve mental clarity. Engaging in various recovery techniques, such as foam rolling, provides relief and supports performance too. By working on both physical and mental aspects, gymnasts fortify their core training regimen significantly.
Progress Tracking and Assessment
To maximize core stabilization effectiveness, consistent progress tracking is fundamental. Gymnasts should regularly assess their core strength and stabilization progress. Simple tests, like timed planks or maximum repetitions of specific exercises, can provide useful insights. Tracking improvements not only motivates athletes but also highlights areas needing attention. Furthermore, utilizing performance metrics helps in adjusting training regimens according to individual needs. This can include varying exercise intensity or volume based on specific goals. When gymnasts identify their weaknesses, they can focus on targeted training to enhance performance. Coaches play a critical role in this process; having a knowledgeable coach provides additional support and feedback. Regular coaching assessments help refine techniques and ensure proper form while executing core-based exercises. Additionally, diversifying core workouts introduces various stimuli, preventing plateaus in progress. Gymnasts may also incorporate element drills to simulate real competition. These drills, combined with core stabilization exercises, create a comprehensive training experience. Ultimately, consistent tracking and assessments form the foundation for achieving peak athletic performance in gymnastics. By making adjustments and staying focused, gymnasts can achieve remarkable growth in their core strength and overall effectiveness.
Functional movement patterns are critical in promoting core stabilization. According to experts, understanding these patterns allows gymnasts to translate stability into athletic performance efficiently. Exercises like squat variations, lunges, and push-up variations create a well-rounded program. These movements engage multiple muscle groups, enhancing the synergy necessary for performing complex gymnastics routines. Furthermore, gymnasts should practice explosive movements involving the core, as this develops power and stability. Plyometric exercises, such as jump squats and box jumps, train the body to stabilize rapidly. Incorporating these explosive elements is especially beneficial for training explosive takeoffs and landings during performances. Moreover, incorporating resistance bands can further enhance core training. Bands provide varying resistance and challenge the muscles during stabilization movements. Furthermore, developing a strong transfer of energy from the lower body through the core is paramount for gymnasts. This interconnectedness entails a focus on both strength and stability. Lastly, mobility exercises should not be neglected, as overall agility contributes to successful performances. While strength is vital, flexibility further promotes stability, restoring a full range of motion essential to gymnastics. Consequently, a well-structured program integrating these elements will optimize performance outcomes.
Injury Prevention and Recovery
Incorporating core stabilization techniques greatly reduces the risk of injuries in gymnastics. Weak core muscles can lead to poor posture and ineffective movement patterns, increasing injury likelihood. Proper alignment maintained through stable core workouts supports the spine and other joints during athletic activities. In this context, establishing injury recovery protocols is also necessary. Gymnasts should recognize the importance of rest days, allowing muscles time to recover and restore. During this period, implementing rehabilitation exercises becomes crucial. Targeting the core helps reestablish strength following injury. Exercises focusing on low-impact movements, such as isometric holds and controlled breathing patterns, offer safe recovery options. Once strength begins to return, introducing gradual loading through controlled exercises assists in muscle rebuilding. In conjunction, maintaining nutrition and hydration is vital. Proper nutrients facilitate efficient recovery following workouts. Additionally, gymnasts should regularly engage in flexibility routines focused on both the core and surrounding muscles. Engaged muscles ensure balanced support, preventing overuse injuries. By understanding these predominant elements, gymnasts can achieve a high level of fitness while minimizing injury risks. Ultimately, core stabilization serves as a protective mechanism in sustaining long-term athletic performance.
Finally, bridging the gap between core stabilization and performance requires a holistic approach. Gymnasts should be willing to adapt their training methods continually to incorporate new strategies. For instance, using technology, such as motion capture systems, helps athletes analyze their movements. Understanding the biomechanics behind movements enhances training effectiveness. Combining these insights with traditional coaching practices creates a comprehensive learning environment. Additionally, participating in workshops and seminars focused on core stability can deepen a gymnast’s knowledge. These resources expose them to advanced techniques and contemporary research developments in training methodologies. Furthermore, fostering a supportive training environment encourages camaraderie among athletes. This creates a culture of mutual benefit, as athletes share insights and techniques to elevate overall performance. Mentoring relationships with experienced gymnasts or coaches can offer valuable guidance for juniors looking to enhance their core training. Incorporating functional training within the holistic regimen ultimately leads to a more complete athlete. Attaining mastery over core stabilization techniques cultivates greater confidence during performances. Moreover, it prepares gymnasts for the demanding nature of competitive gymnastics, ensuring they achieve spectacular results. In conclusion, investing efforts in core stabilization is essential.
In this dynamic realm, mastering these techniques prepares gymnasts for successful careers. With dedication, assessment, and adaptation, remarkable athleticism becomes achievable. Gymnastics is truly an art, and the core serves as its foundation.