Natural Sources of Collagen vs. Supplements: What’s More Effective?
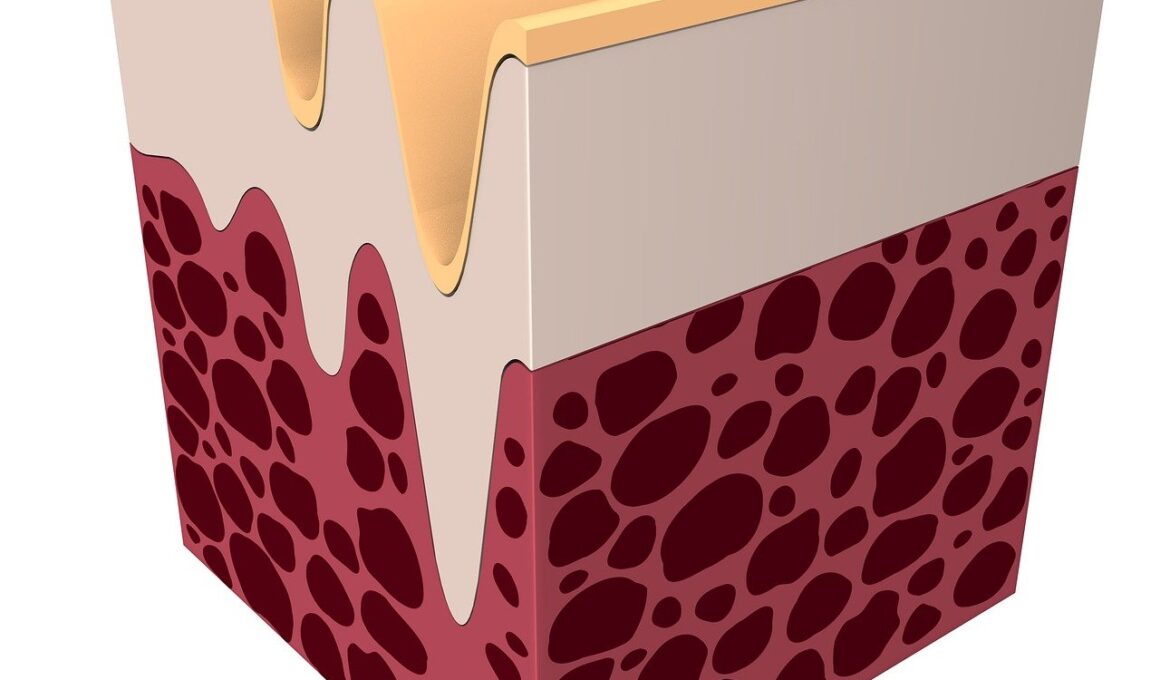
Collagen is a vital protein found in the body, known for its role in supporting joint health. Natural sources of collagen include animal-based products such as chicken skin and fish scales. These sources are protein-rich and provide essential amino acids that your body needs to produce collagen. Additionally, bone broth has gained popularity due to its high collagen content, making it an excellent choice for those looking to improve their joint health naturally. However, not everyone consumes animal products, which limits their access to collagen. Plant-based diets might be deficient in this vital protein, leading many people to seek alternative sources. This is where collagen supplements come in. Accessible in numerous forms, including powders and capsules, they offer convenience for those who can’t meet their collagen needs through diet alone. It’s crucial to explore the effectiveness of both natural sources and supplements. The bioavailability, or how well the body absorbs and utilizes these collagen sources, can vary greatly, warranting a deeper examination of both options to determine what truly benefits joint health and overall wellbeing for different individuals.
Natural sources of collagen are often praised for their authenticity and holistic approach to supplementation. Consuming collagen-rich foods provides other dietary benefits, such as vitamins and minerals that help maintain strong connective tissue. For instance, vitamin C plays a critical role in collagen synthesis and is abundant in fruits and vegetables. Incorporating foods like oranges, strawberries, and leafy greens can enhance collagen production while also supporting joint health. Moreover, natural collagen sources come with additional nutrients, such as zinc and copper, that further contribute to structural health and healing. On the other hand, supplements are formulated to deliver pure collagen directly into the body’s systems, enhancing convenience but sometimes missing the additional benefits present in whole foods. Research on multiple supplement types shows varying efficacy rates, often depending on the form of collagen used. Hydrolyzed collagen, for example, is broken down into smaller peptides, making it easier for the body to absorb. Despite potential effectiveness, choosing between natural sources and supplements can feel overwhelming for those new to this topic, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making in achieving joint health goals.
The Role of Bioavailability
When comparing natural sources of collagen and supplements, bioavailability is a primary concern. Bioavailability refers to the extent and rate at which nutrients are absorbed into the body. In the case of collagen, factors such as the food matrix, preparation method, and individual digestive efficiency significantly influence absorption levels. Studies indicate that collagen derived from animal sources is generally well-absorbed, especially when prepared in broth or similar dishes. In contrast, collagen supplements often use hydrolyzed collagen, resulting in smaller peptide chains that can enhance absorption rates beyond what a natural source may provide. Understanding how different collagen types break down can help consumers select the right option for their health needs. Moreover, combining collagen intake with vitamin C-rich foods can tremendously affect how well the body utilizes collagen. Thus, assessing bioavailability can guide individuals to choose the best method to incorporate collagen into their diets while keeping joint health at the forefront of the decision-making process.
Another consideration when evaluating collagen sources is the quality of supplementation. The supplement industry is vast, with many products attempting to capitalize on the growing interest in collagen for joint health. Not all collagen supplements are created equal, so examining factors such as sourcing, manufacturing processes, and purity is crucial. Opting for high-quality collagen supplements derived from grass-fed or wild-caught sources can ensure higher nutrient density and fewer additives. Transparency in labeling is another vital piece of the puzzle; consumers should check for third-party testing to verify ingredient quality. Furthermore, the presence of additional nutrients in some supplements, such as hyaluronic acid or glucosamine, can complement the collagen and offer enhanced benefits for joint health. Educating oneself about ingredient quality and understanding the reputation of brands can help avoid poor-quality products that may not provide the intended health benefits. A careful selection of collagen supplements can ultimately lead to better outcomes for those looking to support their joint health effectively.
Research and Efficacy
The scientific literature addressing the efficacy of collagen for joint health presents mixed but encouraging findings. Several studies support the claim that collagen supplements promote joint health, showcasing increased mobility and decreased discomfort among participants. For instance, a double-blind study demonstrated significant improvements in knee joint function and pain levels in individuals who took collagen hydrolysate daily over months compared to a placebo group. Moreover, the positive influence of collagen on cartilage regeneration has potential long-term benefits for joint health. It’s essential to understand that while supplements can yield noticeable results, they do work best in conjunction with a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. Maintaining physical activity, consuming anti-inflammatory foods, and remaining hydrated plays a crucial role in nurturing joint health. As research continues to evolve, individuals interested in collagen supplementation should stay informed. Collaborating with healthcare professionals can further guide them based on their specific health needs and conditions.
For those unable to access sufficient natural collagen sources, supplementation may provide the necessary support for joint health. Despite potential benefits, the long-term implications of exclusive reliance on collagen supplements require careful consideration. Some experts emphasize that focusing solely on supplements can lead to nutritional imbalances over time. Emphasizing a diverse diet rich in whole foods alongside supplement intake may be the most beneficial strategy for joint health. By doing so, individuals can enjoy the benefits of collagen while also receiving the full spectrum of essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals needed for overall health and wellness. Regular intake of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can synergize with collagen supplementation for even better outcomes. Prioritizing a holistic approach that combines nutrition, an active lifestyle, and proper hydration can create a strong foundation for joint health. As we learn more about the role of collagen in our bodies, adopting a comprehensive plan centered around healthy eating habits becomes increasingly valuable in reaching health goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both natural sources of collagen and supplements present valid options for promoting joint health. The effectiveness of each approach can vary among individuals, depending largely on dietary habits, overall health, and lifestyle choices. Natural sources offer nutritional diversity, including vitamins that support the entire musculoskeletal system, while supplements provide a direct and concentrated collagen boost. Ultimately, making an informed decision about consuming collagen, whether through natural means or supplements, is vital for anyone seeking improvement in joint health. Consulting with healthcare professionals or nutritionists can help individuals evaluate their personal needs and requirements, tailoring a plan suited to their health goals. Emphasizing a well-rounded approach that blends proper nutrition, physical activity, and supplementation will not only enhance collagen intake but can also optimize joint health and quality of life. As the conversation around collagen continues to grow, staying well-informed will lead individuals towards the best options for themselves and encourage proactive strategies for long-term wellness.
Lastly, those contemplating collagen use should also be aware of the potential side effects and contraindications associated with supplements. Side effects are typically mild but can include digestive discomfort or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. It’s essential to be mindful of these possibilities and consult a healthcare provider if any adverse effects arise. Moreover, the source of collagen can also influence tolerability; for example, marine collagen may not be suitable for individuals with fish allergies. Additionally, understanding the recommended dosage and duration of supplement use is essential to avoid any unnecessary risks. Ultimately, by balancing well-informed choices regarding natural sources and supplements, individuals can take proactive steps toward enhancing their joint health. The key lies in adopting a comprehensive and thoughtful approach, enabling one to reap maximum benefits while minimizing potential downsides associated with collagen consumption, whether derived from food or supplements. Thorough research combined with guidance from professionals will lead anyone pursuing collagen for joint health in the right direction, allowing them to enjoy an active and pain-free lifestyle.