Biomechanics of Upper Limb Rehabilitation After Sports Injury
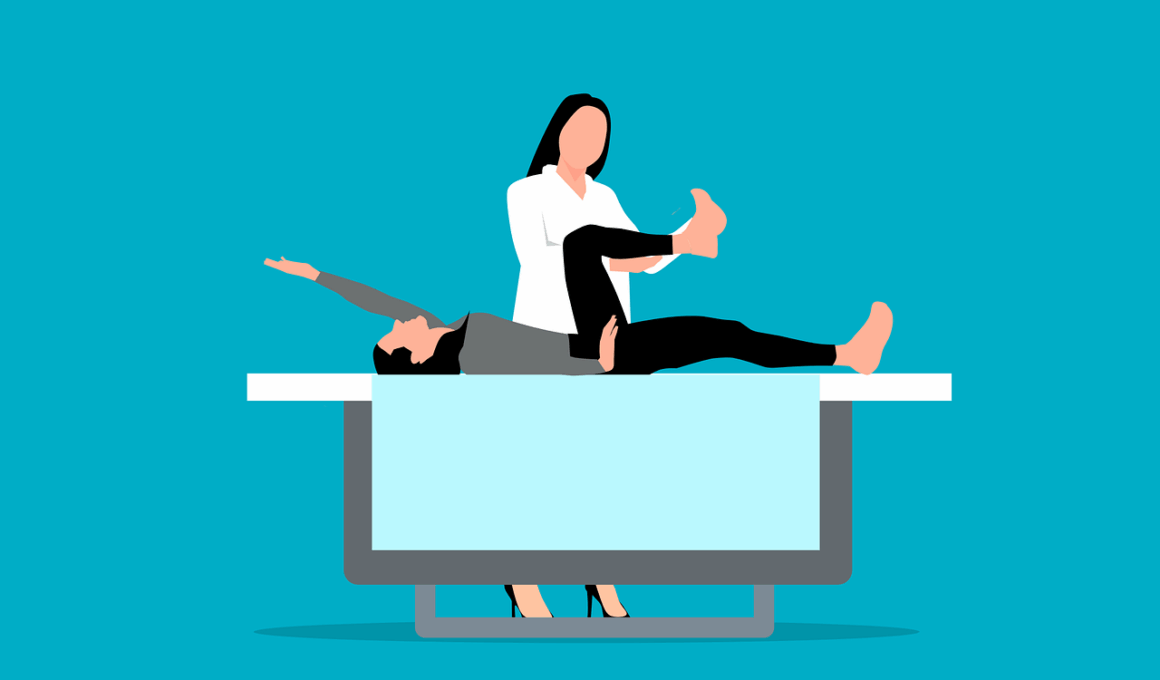
Upper limb injuries are increasingly common among athletes, and understanding the biomechanics involved is crucial for effective rehabilitation. Sports injuries often include fractures, ligament tears, or tendonitis, impacting an athlete’s mobility and performance. Rehabilitation biomechanics focuses on optimizing recovery through tailored movement patterns that facilitate healing. By recognizing the specific injuries athletes face, professionals can develop rehabilitation programs that emphasize proper mechanics, strength training, and flexibility. One key aspect is assessing the range of motion to create a personalized approach. It is essential to analyze how biomechanical factors, such as joint angles and muscle activation, influence recovery rates. In particular, rehabilitation strategies may involve exercises to enhance neuromuscular control, thereby reducing the risk of re-injury. Integrating technology like motion capture systems can provide valuable insights into performance trends and biomechanics. Ultimately, these tools help practitioners adjust rehabilitation protocols according to individual progress, ensuring athletes regain their peak performance levels. This not only aids in physical recovery but also builds athletes’ confidence in the function of their rehabilitated limbs, setting a solid foundation for their return to competitive sports once healed and strong.
Understanding the complexities of rehabilitation requires knowledge of how different muscle groups interact during functional movements post-injury. The upper limb consists of bones, muscles, and joints that work synergistically to perform tasks. Rehabilitation biomechanics emphasizes the importance of these interactions to restore functionality. When an athlete sustains an injury, specific muscles may weaken or become inhibited, altering their normal movement patterns. Rehabilitation focuses on restoring strength, coordination, and proprioception, crucial for preventing compensatory movements. Incorporating exercises such as resistance training and stability work can effectively target these deficits. Performing dynamic activities rehabilitates the intricate balance between agonist and antagonist muscle groups, enhancing overall upper limb functionality. Emphasizing specific joint movements, such as shoulder abduction or elbow flexion, allows therapists to design focused programs that improve athletic performance. A thorough understanding of the kinetic chain aids in developing protocols to optimize recovery rates. Furthermore, monitoring progress through consistent assessments ensures adaptations in the rehabilitation approach according to the athlete’s needs. By prioritizing these biomechanical principles, practitioners facilitate a smoother transition back to sport and improve outcomes in long-term recovery.
Key Biomechanical Principles in Rehabilitation
Key biomechanical principles guide rehabilitation strategies for athletes recovering from upper limb injuries. Force distribution is one concept that emphasizes how forces interact within the body’s joints and muscles during rehabilitation. Even simple movements generate internal and external forces, significantly affecting recovery rates. Understanding these dynamics ensures that rehabilitation exercises enhance restoration while avoiding undue stress on injured areas. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment throughout the recovery process is essential. Misalignment can lead to compensatory patterns that exacerbate injuries or create new ones. Effective rehabilitation incorporates strategies, such as targeted exercises or spinal adjustments, preventing misalignment to optimize function. Implementing progressive loading strategies is another biomechanical principle, allowing gradual increase in intensity while monitoring for pain or discomfort. Educating athletes on body mechanics serves as a critical component of rehabilitation, allowing them to actively participate in their recovery. Moreover, this understanding aids in injury prevention during their return to sport, ultimately promoting resilience against future injuries. By integrating these principles into tailored rehabilitation programs, professionals can enhance healing efficiently and safeguard against long-term complications in athletic performance and return to competition.
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing rehabilitation outcomes for upper limb injuries. Advanced tools, such as wearable devices, provide continuous monitoring of biometric data, allowing for real-time adjustments during recovery. Motion analysis systems enable therapists to visualize and assess movement mechanics. This data-driven approach enhances communication between athletes and healthcare professionals, promoting informed decision-making regarding rehabilitation protocols. Additionally, virtual reality training has emerged as an innovative strategy to improve engagement during rehabilitation sessions. Athletes can practice movements in a controlled environment, enhancing their proprioception and coordination skills. Additionally, gamification techniques are increasingly utilized to motivate athletes during rehabilitation, making the process more dynamic and encouraging adherence to prescribed exercises. Feedback obtained from these technologies allows therapists to modify exercises according to established benchmarks, promoting optimized rehabilitation programs. This personalized approach ensures that characteristics such as fatigue levels or pain are considered, facilitating a more comprehensive perspective on each athlete’s recovery journey. All these innovations together aim to enhance not just the rehabilitation process but significantly improve the outcomes, allowing athletes to return to their respective sports with enhanced confidence in their physical capabilities.
Therapeutic Exercises and Their Impact
Therapeutic exercises form the foundation of rehabilitation for athletes recovering from upper limb injuries. Specific exercises target the muscles’ functional capabilities, focusing on strength, flexibility, and coordination. For instance, resistance band exercises may be incorporated to improve muscle strength gradually, while stretching exercises work on restoring flexibility. These exercises help develop balance and stability, essential for effective movement, especially in high-performance sports. Functionally integrated movements can also simulate the demands placed on the upper limb during sports, ensuring that athletes regain their confidence and readiness to compete. As athletes progress, more complex movement patterns are introduced, with an emphasis on neuromuscular control. Gradual increases in weight and repetitions stimulate muscle growth, which translates to improved performance when returning to the sport. Moreover, balancing muscle engagement across all functional planes aids in creating a solid foundation for long-term athletic longevity. Regular assessments allow therapists to adapt programs in response to the athlete’s changing needs, ultimately enhancing recovery. With the right combination of therapeutic exercises and professional guidance, athletes can achieve a successful return to their sports with minimized risk for future injuries.
Besides physical rehabilitation, addressing the psychological aspect is crucial in upper limb recovery post-injury. Sports injuries can lead to a significant psychological toll, including anxiety, depression, or fear of re-injury. Together with physical rehabilitation, mental health support can expedite the recovery process. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) may be employed to help athletes navigate their emotional responses throughout rehabilitation. Creating a supportive environment encourages open communication between athletes, therapists, and coaches, emphasizing progress and successes along the way. Furthermore, visualization techniques can enhance performance through mental rehearsal, increasing athletes’ confidence during re-entry into competitive sports. Setting realistic goals within both physical and mental rehabilitation frameworks provides a structured approach, allowing athletes to measure progress consistently while acknowledging small victories. This mental component aligns with the importance of motivation, leading to better participation and outcomes throughout the rehabilitation journey. Ultimately, fostering a positive mindset keeps athletes engaged while minimizing the psychological burden associated with sports injuries. By combining physical and mental strategies, we can create a more holistic approach that supports athletes’ overall well-being during recovery from upper limb injuries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biomechanics plays a pivotal role in upper limb rehabilitation after sports injuries. With a focus on understanding the interactions of muscles, joints, and movement patterns, rehabilitation professionals can create effective recovery strategies. By integrating advanced technology and therapeutic exercises into rehabilitation protocols, significant improvements can be made in the athlete’s physical performance and psychological well-being. It is also essential to ensure that all rehabilitation programs prioritize individualized care, paying attention to the specific needs of each athlete. By establishing solid communication between therapists and athletes, tailored approaches can be developed that meet unique recovery requirements. This aspect is critical for fostering trust and belief in the rehabilitation process. Furthermore, addressing both physical and mental dimensions enhances the overall efficacy of rehabilitation, ensuring a smoother transition back to competitive sport. By adhering to biomechanical principles and using innovative therapeutic techniques, the road to recovery can be optimized, giving athletes the best chance for a successful return to their respective sports. Ultimately, well-planned rehabilitation strategies build a foundation that not only aids in physical recovery but also instills confidence, leading to better long-term outcomes and resilience against future injuries.
In conclusion, biomechanics plays a pivotal role in upper limb rehabilitation after sports injuries. With a focus on understanding the interactions of muscles, joints, and movement patterns, rehabilitation professionals can create effective recovery strategies. By integrating advanced technology and therapeutic exercises into rehabilitation protocols, significant improvements can be made in the athlete’s physical performance and psychological well-being. It is also essential to ensure that all rehabilitation programs prioritize individualized care, paying attention to the specific needs of each athlete. By establishing solid communication between therapists and athletes, tailored approaches can be developed that meet unique recovery requirements. This aspect is critical for fostering trust and belief in the rehabilitation process. Furthermore, addressing both physical and mental dimensions enhances the overall efficacy of rehabilitation, ensuring a smoother transition back to competitive sport. By adhering to biomechanical principles and using innovative therapeutic techniques, the road to recovery can be optimized, giving athletes the best chance for a successful return to their respective sports. Ultimately, well-planned rehabilitation strategies build a foundation that not only aids in physical recovery but also instills confidence, leading to better long-term outcomes and resilience against future injuries.