Hydration and Gut Microbiome: Influence on Digestion and Sport Performance
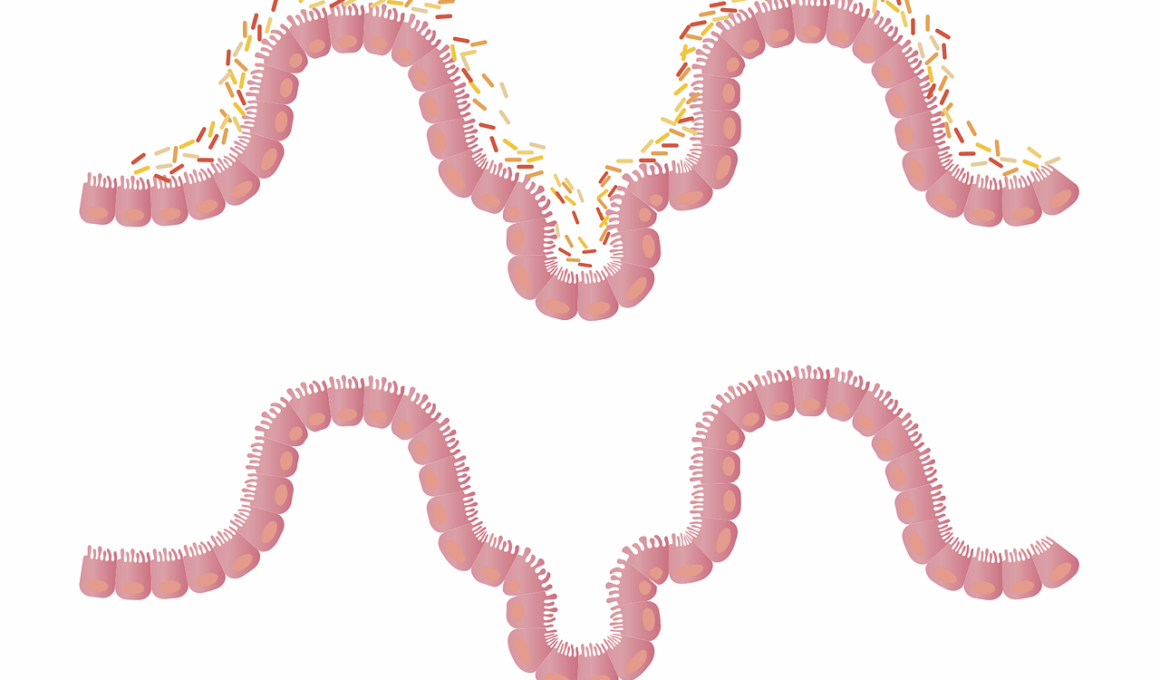
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in digestion and overall health. Studies indicate that the balance of microbes in our intestines can significantly impact nutrient absorption, immune function, and even athletic performance. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining this delicate ecosystem. Adequate water intake helps to ensure that gut bacteria thrive, promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption. Furthermore, dehydration can lead to an imbalance in gut flora, potentially causing digestive issues such as bloating or constipation. Hydrated microbiomes also contribute to enhanced athletic performance by optimizing energy levels and reducing fatigue. Athletes, in particular, must prioritize hydration to ensure their bodies function at peak performance. This means not only drinking enough water but also considering electrolyte balance to support gut health. Including beverages rich in electrolytes can enhance hydration strategies, promoting a favorable gut environment. Optimal hydration can also result in better recovery times, making it essential for athletes to stay well-hydrated before, during, and after training sessions. Ultimately, the synergy between hydration, gut microbiome, and performance is essential for anyone looking to improve their digestive function and athletic output.
The Role of Water in Digestive Processes
Water plays an indispensable role in various digestive processes, aiding in the breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients. It is crucial for saliva production, which initiates the digestion of carbohydrates and creates a medium for taste. The stomach also relies on water to maintain a proper pH level, facilitating the action of digestive enzymes. Additionally, water helps transport nutrients throughout the body, ensuring that cells receive what they need to function efficiently. When the body is dehydrated, not only does digestion slow down, but the intestines become less effective in absorbing nutrients, leading to deficiencies. Furthermore, sufficient hydration is necessary to create the mucous lining in the gut, which protects against irritants and supports overall gut health. This protective barrier helps to maintain a balanced microbiome by preventing harmful bacteria from flourishing. One study noted that participants who maintained proper hydration reported fewer digestive discomforts. Moreover, staying well-hydrated can help to prevent constipation by softening stools and promoting regularity. Therefore, drinking enough water daily is fundamental for both optimal digestion and nutrient utilization in the body, enhancing overall well-being and performance throughout the day.
In addition to basic hydration, the timing of water intake can affect digestion significantly. It’s advantageous to drink water before, during, and after meals to optimize digestive efficiency. Sipping water before meals can prepare the digestive system for food intake by stimulating saliva production and ensuring adequate stomach acid levels. Furthermore, drinking water during meals can aid in breaking down food particles and facilitating easier swallowing. However, it’s essential to strike a balance; excessive water intake during meals can dilute gastric juices, potentially impairing digestion. The digestive tract requires a certain concentration of enzymes and acids to effectively break down food, so moderation is key. Post-meal hydration is equally important; water helps flush out toxins and facilitates the absorption of nutrients. Additionally, replenishing lost fluids after meals aids in the maintenance of regular bowel movements, further supporting gut health. For optimal digestive function, incorporating water-rich foods into meals, such as fruits and vegetables, can enhance hydration. Foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges provide not only hydration but also essential vitamins and minerals beneficial for digestion and overall health.
Effects of Dehydration on Gut Health
Dehydration can have pronounced negative effects on gut health and overall function. Insufficient fluid intake may lead to complications such as constipation, which is notably common and uncomfortable. When the body lacks water, the colon absorbs excess fluid from waste, resulting in harder stools that are difficult to pass. Moreover, chronic dehydration can alter gut microbiome composition, giving rise to harmful bacteria’s overgrowth, which can disrupt digestive processes. Research suggests that a balanced gut microbiome thrives on hydration; thus, any disturbances can adversely affect digestion and nutrient absorption. This imbalance may lead to various symptoms, such as bloating, gas, and even irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Furthermore, dehydration impacts the body’s ability to manage inflammation, which is often exacerbated by an unhealthy microbiome. Maintaining proper hydration levels supports both the garden of microbial species and the structure of the gut lining, preventing the permeability issues that can lead to leaky gut syndrome. Therefore, ensuring adequate water consumption is a simple yet effective strategy to promote a healthy gut environment, protect digestive health, and support overall physical well-being.
Electrolytes, alongside water, are also critical for hydration and gut health. These minerals help maintain fluid balance and are essential for muscle function and sports performance. Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium contribute to maintaining hydration levels, particularly during intense physical exertion. When exercising, especially in hot environments, the body loses not only water but also electrolytes through sweat. Replenishing these lost minerals is crucial to prevent muscle cramps and maintain optimal bodily functions. Incorporating electrolyte-rich beverages or supplements into a hydration strategy may enhance gut health and performance. Moreover, certain electrolytes have been shown to support gut barrier integrity, helping to maintain a healthy microbiome. Foods like bananas, coconut water, and sports drinks can provide quick sources of electrolytes for athletes. Additionally, consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods can naturally replenish necessary minerals for hydration. Monitoring and adjusting electrolyte intake can further optimize hydration strategies to enhance performance in both training and competition. By understanding and implementing effective hydration practices, individuals can support overall health and athletic performance while promoting optimal gut function.
Hydration Strategies for Athletes
Athletes face unique challenges when it comes to hydration and gut health, as their physical demands require tailored strategies. First and foremost, hydration strategies should begin before training starts. Proper hydration before a workout prepares the body for exertion and supports optimal performance. It’s advisable for athletes to drink water consistently throughout the day, ensuring that they begin activities in a well-hydrated state. During exercise, it’s essential to have a hydration plan that includes regular intake of water or electrolyte-rich beverages to replenish lost fluids. This is particularly crucial for endurance athletes or those training in hot conditions. After training sessions, rehydration should include not only water but also nutrients to aid recovery. Nutrient-rich snacks containing carbohydrates and proteins, paired with hydrating fluids, can boost recovery and optimize gut health. Furthermore, athletes should pay attention to their personal hydration needs, as they may vary significantly based on factors such as intensity, duration, and climate conditions. By developing personalized hydration strategies, athletes can maximize their performance while supporting their gastrointestinal health and overall well-being.
In conclusion, hydration is integral to maintaining gut microbiome health and enhancing digestive processes, ultimately influencing athletic performance. The relationship between the gut microbiome, hydration, and sports cannot be overstated. Focus on adequate water intake and maintaining electrolyte balance is essential for digestive efficiency and optimal performance. Each aspect—from timing and quantity of fluid intake to choosing water-rich foods—plays a role in ensuring gut health. Moreover, athletes must develop specific hydration strategies tailored to their needs and moderate their fluid intake based on activities and environmental conditions. Additionally, understanding the effects of dehydration on gut microbiome composition and gastrointestinal function can guide effective hydration practices. Athletes may benefit from considering electrolyte supplements and nutrient-dense foods as part of their recovery protocols. Emphasizing hydration as a critical aspect of training regimens is necessary for achieving peak performance and maintaining digestive health. Regularly evaluating hydration practices can lead to improved health outcomes, enhancing performance levels for athletes across various sports. Ultimately, a strong foundation in hydration strategies opens the door to better digestion and elevated athletic performance, promoting long-term health and well-being.