Understanding Swimmer’s Shoulder: Causes and Prevention
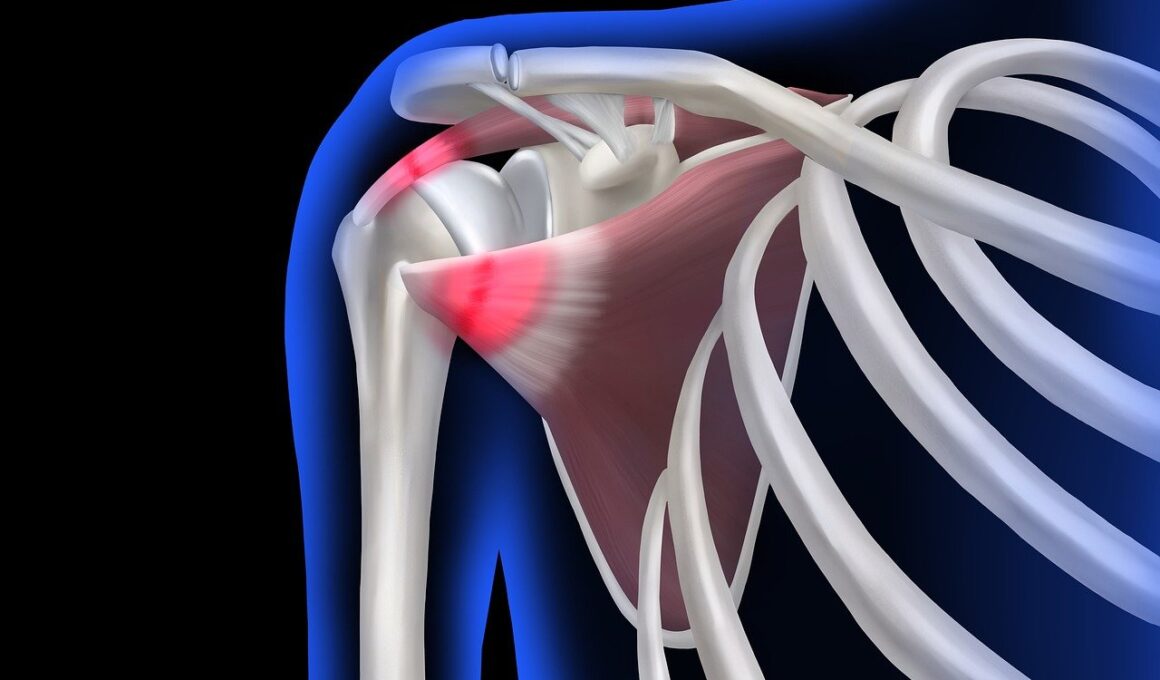
Swimmer’s shoulder is a term often used to describe a common injury experienced by many swimmers, characterized by shoulder pain specifically during certain shoulder movements. This type of injury can severely impact an athlete’s ability to train and compete effectively, often leading to frustration. Key reasons swimmers develop this condition include repetitive strain and improper technique during strokes. Over time, performing the same motions repeatedly without proper recovery and strength training can lead to inflammation of the shoulder tendons. These inflammatory conditions can cause pain, reduced range of motion, and weakness in the affected shoulder. For many competitive swimmers, these symptoms can become debilitating, affecting their overall performance in the pool. It is crucial to recognize the early signs of swimmer’s shoulder, such as persistent pain, and to seek professional assistance. Coaches and athletes should collaborate to ensure proper mechanics and to implement preventive strategies. In understanding this condition, swimmers can better appreciate their bodies’ limits and act accordingly.
Identifying the Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of swimmer’s shoulder can vary significantly among individuals, making it essential for swimmers to pay close attention to any discomfort they might feel. Typically, pain may manifest in the front or back of the shoulder, particularly during overhead movements. Other symptoms include tenderness around the shoulder joint, swelling, and a reduced range of motion, which could significantly impact a swimmer’s performance. Some may also experience a clicking sound within the joint during movement, indicating potential underlying issues. If an athlete notices these symptoms, it is important not to ignore them. Swimmers should consult a medical professional for a thorough assessment and diagnosis. Early intervention can lead to swift recovery and help prevent chronic issues from forming. Additionally, maintaining open communication between the swimmer and coach regarding any pain or discomfort is vital in appropriately addressing these concerns. Ignoring symptoms can worsen the condition, leading to lengthy downtime and preventing the athlete from participating in competitions. Therefore, it’s crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in addressing any signs of swimmer’s shoulder.
To help prevent swimmer’s shoulder, swimmers should consider integrating appropriate warm-up routines before getting into the water. Warm-ups should include both dynamic stretches and strength-building exercises targeting the shoulder muscles. Equally important is incorporating a cooldown routine after swimming sessions, promoting flexibility and recovery. A well-structured training plan should be designed with a balanced approach to strength and endurance, ensuring muscles are conditioned to handle the demands placed upon them. Additionally, swimmers should regularly assess their stroke technique, as improper mechanics can contribute significantly to shoulder strain. Working with a knowledgeable coach to refine techniques can facilitate improved performance while reducing injury risks. Furthermore, swimmers should listen to their bodies and incorporate adequate recovery time throughout their training. Ensuring hydration, good nutrition, and appropriate rest promotes muscle repair and reduces the risk of overuse injuries. Swimmers should also consider cross-training activities that support overall shoulder strength and flexibility without the repetitive strain associated with swimming. These preventative measures are vital in maintaining health and longevity in the sport.
Strength and Flexibility Training
Incorporating a focused strength and flexibility training regimen can significantly contribute to preventing swimmer’s shoulder. These exercises help build a stable foundation for the shoulder joint, making it more resilient against injuries. Swimmers should prioritize strengthening exercises that target not only the shoulder muscles but also the core and back muscles. Balancing strength across different muscle groups can reduce the risk of imbalances that often lead to injuries. Exercises such as rotator cuff strengthening, shoulder raises, and rows will aid in developing stability. Furthermore, flexibility routines involving dynamic stretches, yoga and yoga-inspired movements can enhance the range of motion in the shoulders. These routines encourage better joint mechanics while swimming. Targeting muscles like the pectoralis major and other supporting muscles helps maintain the shoulder in a healthy position during strokes. Consistently dedicating time to these training sessions both on land and in the water will develop the fundamental strength needed for injury prevention. Swimmers should also focus on proper breathing techniques during strength exercises, promoting overall body awareness and control.
Another critical aspect of preventing swimmer’s shoulder is understanding when to seek professional help. If a swimmer is exhibiting signs of pain or discomfort, an accurate diagnosis from a sports medicine professional is imperative. This diagnosis will determine whether the swimmer is dealing with an overuse injury, inflammation, or a more serious condition requiring specific feedback. Many coaches can provide initial recommendations, but consulting a physical therapist or sports physician will provide a thorough evaluation of the swimmer’s functional movement and biomechanics. Regular assessments conducted by professionals can help identify potential weaknesses in strength or flexibility and facilitate a targeted rehabilitation program. Athletes should take an active interest in maintaining their shoulder health, understanding the importance of listening to their bodies. Engaging in preventative exercises and adhering to professional recommendations can be essential in stopping injuries. Ultimately, maintaining open communication with coaches, trainers, and medical professionals will enhance a swimmer’s ability to train safely and effectively. This proactive approach is crucial in sustaining athletic performance and enjoyment of the sport.
Nutrition and Hydration’s Role
Nutritional choices and hydration levels play a vital role in injury prevention, particularly when it comes to conditions like swimmer’s shoulder. Swimmers should prioritize a balanced diet, rich in essential nutrients such as vitamins and minerals necessary for muscle repair. Consuming sufficient protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats supports energy needs and recovery from workouts. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory properties can promote healing and reduce any inflammation already present. Additionally, adequate hydration is critical for muscle function and overall performance. Dehydrated muscles are more prone to strain and fatigue, potentially leading to injuries. Thus, athletes should develop a hydration plan tailored to their training routines and individual body requirements. During swimming sessions, hydrating appropriately can keep muscles in optimal condition. Furthermore, incorporating electrolytes in recovery drinks or snacks can restore lost minerals after rigorous workouts. By understanding the relationship between nutrition, hydration, and injury prevention, swimmers can make informed choices that support overall performance and health, allowing them to train efficiently while minimizing injury risks.
In summary, swimmer’s shoulder is a preventable condition that requires diligence from athletes and coaches alike. By being proactive about identifying early signs and symptoms of pain, developing preventative training habits, and incorporating a balanced diet, swimmers can significantly reduce the likelihood of injuries. Emphasizing strength and flexibility can build resilience within the shoulder joint and enhance overall performance in the water. Awareness of correct techniques and approaches during training sessions is crucial for injury prevention as well. Swimmers should also remain open to adjusting their routines, including seeking professional assistance when necessary, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of how best to care for their bodies. In coaching, communication about any pain or discomfort must be a priority, leading to collaborative approaches to prevent swimmer’s shoulder. Moreover, athletes must foster a mindset focused on their overall health and well-being. Educating oneself and others about the risks associated with swimmer’s shoulder opens the door to creating a safer environment for all. Ultimately, these practices and awareness will culminate in healthier, happier swimmers who thrive in their sport.
Conclusion
As part of a swimmer’s commitment to excellence, understanding swimmer’s shoulder and taking necessary preventive measures are essential components of a successful training regimen. Addressing the risk factors associated with this common injury should always be a priority for swimmers of all levels. By practicing proper techniques, maintaining strength and flexibility, ensuring a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, athletes can successfully navigate their swimming journeys without falling victim to unwanted injuries. Ongoing education about swimmer’s shoulder, its prevention, and the body’s mechanics foster an environment where swimmers are better equipped to maintain high levels of performance and comfort in the water. Consequently, cultivating healthy habits empowers athletes to pursue their passion sustainably and efficiently. In fostering a culture of awareness around swimmer’s shoulder, swimmers can support one another in achieving athletic goals while minimizing injuries. Ultimately, prevention is the key to long-term success in swimming. By committing to these practices, swimmers can enjoy the sport they love while continuously improving their skills in a safe, enjoyable manner.