Developing Mindfulness Habits in Early Childhood Education
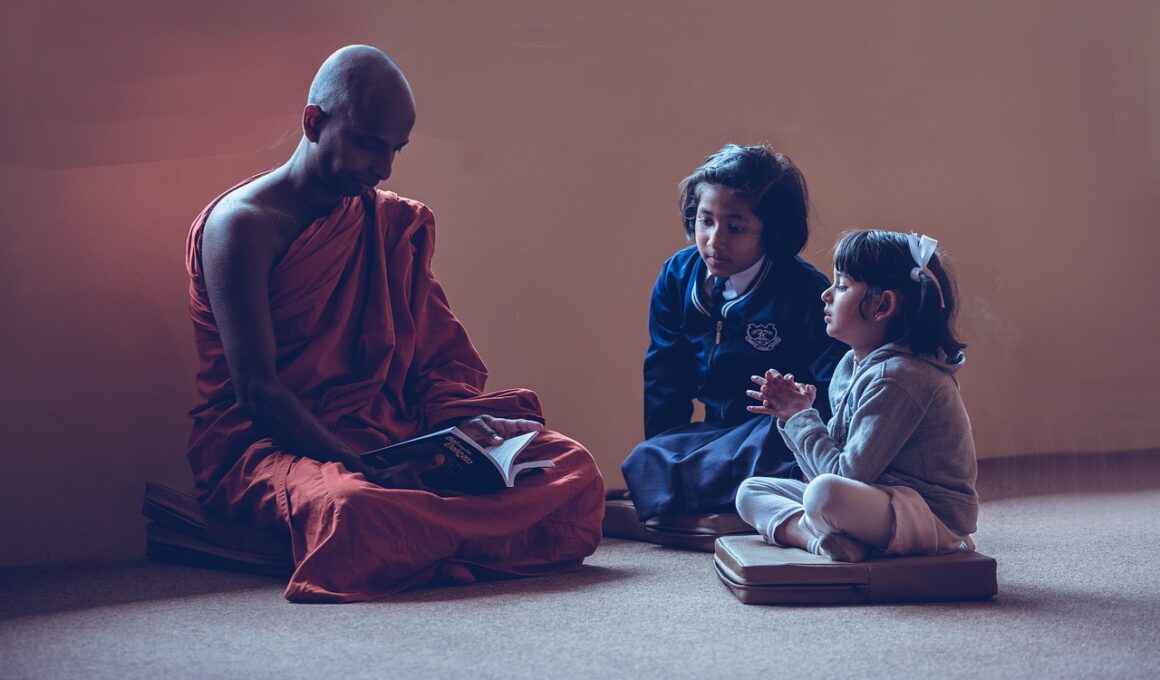
Mindfulness in education has gained popularity, especially in early childhood education. Research highlights the importance of fostering mindfulness habits among young children to enhance their emotional intelligence. Schools are increasingly incorporating meditation practices into classrooms. Young learners benefit significantly from these practices, as they encourage focus and attention. Mindfulness exercises help children understand their own emotions, leading to greater social interaction and emotional regulation. Engaging in mindfulness activities helps them develop a sense of self-awareness. Incorporating techniques like deep breathing can create a calm classroom environment. Moreover, teachers play a crucial role in modeling mindfulness for students. When educators practice mindfulness, they positively influence their students’ attitudes and behaviors. Implementing structured programs allows for consistent practice of mindfulness habits. Additionally, parents should be involved in reinforcing the practices learned at school within home environments. This holistic approach ensures children experience the benefits of mindfulness comprehensively. Mindfulness in education is not just a trend; it is becoming a fundamental aspect of holistic development in children, preparing them for the complexities of modern life, fostering resilience, empathy, and improving their overall well-being.
Mindfulness activities in early childhood education can vary in nature and execution. Schools often design curriculums that include a variety of interventions, tailored to suit the developmental stages of children. Common practices include guided imagery, breathing exercises, and even mindful moving activities. These activities serve dual purposes of improving focus and facilitating emotional processing. For instance, engaging children in nature walks encourages observation and reflection. Simple practices like sitting quietly and listening to sounds in nature can cultivate a sense of presence. Teachers can also incorporate storytelling that promotes mindfulness themes, enhancing imagination while teaching important life skills. Establishing a dedicated time for mindfulness within the school day ensures that all children participate actively. It’s crucial that such practices are approached with age-appropriate techniques, keeping children engaged and attuned. Parents can support this by practicing mindfulness at home as well. Creating family mindfulness traditions can strengthen bonds and inspire children. Consistency in practice will yield the most significant results, as children learn to integrate these practices into daily routines. Building a foundation in mindfulness early in life equips children with vital skills for academic success and personal well-being.
Benefits of Mindfulness in Early Childhood Settings
The implementation of mindfulness in early childhood education offers numerous benefits. Research indicates that children who participate in regular mindfulness practice demonstrate improved attention, reduced impulsivity, and enhanced emotional regulation. These benefits lead to better classroom behavior and academic performance. Mindfulness also fosters better relationships among peers, as children learn empathy through understanding their own emotions and those of others. Furthermore, engaging in mindfulness promotes resilience. Children learn to cope with stress and challenges that arise in daily interactions, equipping them with problem-solving skills. Incorporating creative approaches to mindfulness, such as art and music, helps children express their feelings more effectively. Activities like yoga can also be beneficial, improving physical health and promoting body awareness among young individuals. Importantly, these practices assist in creating a positive classroom environment, where students feel safe and supported. A mindful classroom reduces anxiety levels, creating a conducive learning environment. As the demand for social-emotional learning increases, incorporating mindfulness makes early childhood education more relevant and adaptable to current educational needs. The long-term benefits are seen in children’s preparedness for life’s various challenges.
While implementing mindfulness practices in early childhood education, it is essential to consider the qualifications of educators. Teachers need appropriate training to guide mindfulness exercises effectively. Professional development opportunities focusing on mindfulness in education can be invaluable. Educators who understand the principles of mindfulness can better facilitate experiences for children, ensuring the practices are beneficial and enjoyable. Collaboration among staff also enhances the mindfulness experience in schools. By working together, teachers can share techniques and activities that resonate well with students. Schools should create a supportive culture that encourages staff to integrate mindfulness practices into their daily routine. Developing a united front enables all teachers to reinforce similar messages to students. Moreover, parent involvement in these programs solidifies the support structure for children. Workshops or informational sessions on mindfulness for parents can foster understanding. These sessions can teach parents how to practice mindfulness at home, creating an environment where children feel supported and understood. This synergy between home and school is essential for maximizing the benefits of mindfulness practices in children’s lives.
Challenges in Integrating Mindfulness
Integrating mindfulness into early childhood education does come with challenges. One significant obstacle is time constraints within the curriculum. Many educators feel overwhelmed with existing academic demands and struggle to allocate time for mindfulness practices. However, research shows that even short sessions can be impactful if conducted consistently. Another challenge is the need for specialized training for educators. Not all teachers are trained in mindfulness techniques, which may lead to inconsistent practices. Schools need to prioritize professional development focusing on mindfulness to overcome this barrier. Additionally, schools may face resistance from parents unfamiliar with the concept. Educating parents about the benefits of mindfulness is crucial for fostering acceptance. Furthermore, it’s important to address potential misconceptions related to mindfulness practices. Some individuals may view mindfulness as impractical or unrelated to education. Effectively communicating the benefits and providing evidence-based research can encourage more extensive implementation. Developing a supportive network within the community can also help address challenges. Engaging local organizations that focus on wellness can provide resources and support for schools trying to integrate mindfulness practices effectively.
Maintaining mindfulness practices becomes easier with a strategic plan. Schools should evaluate their mindfulness programs regularly to ensure their effectiveness. Feedback from both educators and students can provide insights into what works and what requires adjustment. Establishing clear goals for mindfulness practices is vital for evaluating progress. Monitoring improvements in student behavior and emotional intelligence can help determine the impact of mindfulness initiatives. Educators can also explore different teaching methodologies to engage students uniquely. Techniques such as gamification or using technology can make mindfulness practices more appealing to young learners. Incorporating multimedia resources helps maintain attention and appeal to various learning styles. Additionally, forming mindfulness clubs within schools can create student-led initiatives that promote mindfulness among peers. Encouraging older students to mentor younger ones in mindfulness practices creates a community-based approach. This systematic evaluation encourages continuous improvement in mindfulness practices. A structured, consistent schedule should be maintained to foster long-term engagement from both teachers and students alike. Over time, these practices may significantly enhance students’ overall awareness, fostering a community dedicated to emotional well-being and resilience.
Conclusion: Future of Mindfulness in Education
The future of mindfulness in early childhood education looks promising as more schools recognize the importance of these practices. Integrating mindfulness offers children vital skills that enhance their emotional intelligence, resilience, and academic performance. As more educators receive training and resources become more readily available, the scope and effectiveness of mindfulness practices will likely expand. These practices will continue to evolve, adapting to the changing landscape of education. Innovations and research will provide continuous insight into improving mindfulness habits for young learners. Schools that prioritize mindfulness will cultivate environments rooted in compassion and understanding. By building these foundations in early education, we equip children with the tools necessary for navigating life’s challenges. The ripple effects of mindfulness established early on can extend beyond the classroom, influencing family dynamics and future societal interactions. As mindfulness becomes more mainstream, collaborating with communities, organizations, and experts will enhance its implementation. This collaborative approach will ensure diverse perspectives are integrated, catering to various needs. Ultimately, prioritizing mindfulness in education will enable generations of children to thrive, creating a more compassionate and mindful society.
Establishing mindfulness in early childhood education supports holistic development. Benefits accrue not only to children but also to educators and families involved. Fostering awareness and emotional growth early in life contributes positively to future learning experiences. As we progress, we should practice consistent reflection on the methods we utilize in mindfulness education to encourage continued refinement and effectiveness.